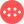
Thermal imaging is a fast, effective solution for helping firefighters tackle blazes.
Firefighters can use thermal imaging cameras (TICs) to detect hotspots and help them in emergency situations.
The high cost of early TICs meant that initial uptake was slow. As the price has come down, the technology has become more affordable and has gone from one camera per fire station to one camera per team and now to one camera per firefighter. At the same time, new tools such as drones and robots equipped with thermal cameras have emerged to help firefighters in their work.
These thermal fire cameras for firefighters can detect infrared rays and were devised using robust materials perfectly suited to the difficult working conditions of the emergency services.
They have been ergonomically designed with and for firefighters, ensuring they can be held comfortably and securely.
Thermal imaging cameras can therefore be used in a wide range of domains: so, what equipment is available to firefighters today and what are the key features of this technology that help them respond to emergencies?
Equipment
A range of equipment featuring thermal cameras is available today to firefighters for observing fires from the inside, outside, and from above.
- TIC (handheld or on a helmet)
Handheld thermal cameras help firefighters deal with fires strategically and enable them to easily maneuver through smoke to save lives. The cameras are compact and robust. They are lightweight and easy to hold, even when wearing bulky gloves.
Firefighters can also deal with the complexities of finding and extinguishing fires by using infrared thermal cameras attached to or even embedded in their helmets, which gives them greater freedom of movement.
The latest fire trucks now have integrated thermal cameras: they are usually positioned at the front of the vehicle, providing a wide field of vision that helps to fully assess the situation. These embedded cameras are very compact and lightweight, making them easy to install in emergency vehicles. They are robustly built, protecting the camera from humidity and water. They do not require any special maintenance and provide excellent images.
A thermal camera mounted on an airborne device or small drone provides a low-angle view of the roofs and upper floors of tall buildings. These devices can help accurately map the affected areas when dealing with large fires spread over vast areas. Among other things, drone-mounted thermal cameras can also help monitor how fires are progressing and detect the intensity of a blaze from a distance.
The need to intervene in hostile settings has led the emergency services to use increasingly innovative tools and technologies. Robots equipped with thermal cameras can be deployed to advance through difficult environments: they can explore dangerous settings before teams intervene. Some robots can go upstairs, climb over small obstacles, and take photos. They are steered like a drone and are linked to a touchscreen control panel. They are an alternative option that limits risk taking. Parisian firefighters use them, and when Notre Dame caught fire in 2019, their robot was the only thing capable of penetrating the blaze. Colossus, which weighs 500 kg, was sent right into the middle of the cathedral and helped save precious time by extinguishing the flames and lowering the temperature inside the nave.
Two types of camera are available to firefighters:
- Decision-making cameras that help evaluate and analyze the fire. These tactical thermal cameras provide firefighters with a large amount of information, helping them stay on top of the situation. High resolutions and high frame rates make these cameras effective tools for the person making decisions.
- Situation awareness cameras can detect hotspots and victims. They help firefighters navigate through the rapidly changing conditions of a fire. They are compact tools designed to support teams in extreme situations such as poor visibility and critical emergencies so they can know where they are, locate victims, and get out of the building. Firefighters can also use them for responding to other emergencies, such as road accidents.
To learn more, download our free infographic with the latest infrared market figures. This 2022 update is broken down by vertical and geographical markets.

The technology’s key features
Thermal cameras have become indispensable for any team intervening in a critical situation.
They help firefighters act quickly while ensuring they stay safe and responsive in an emergency. Infrared can be used to visualize hotspots invisible to the naked eye with a unique level of sensitivity and precision.
When firefighters are on rescue missions or extinguishing fires, infrared technology helps them to:
- See through even thick smoke. Thermal imaging is the only technology that can do this.
- See in a very hot environment (> 1200°C).
- Locate victims.
- Identify residual hotspots after a fire has been extinguished, particularly in forests or industrial settings, and see if a fire may have restarted.
Myriad technological advances mean that firefighters can now use tools that make them more efficient and able to respond faster. Technological support helps teams considerably with the hazardous work of fighting fires by limiting the risk to human lives and materials. Drones and robots equipped with thermal cameras today offer undeniable additional advantages that help certain dangerous tasks be carried out without deploying personnel. The future promises further incredible advances with the development of thermal imaging via satellite to monitor the starting points of forest fires from space.
To learn more, download our free infographic with the latest infrared market figures. This 2022 update is broken down by vertical and geographical markets.